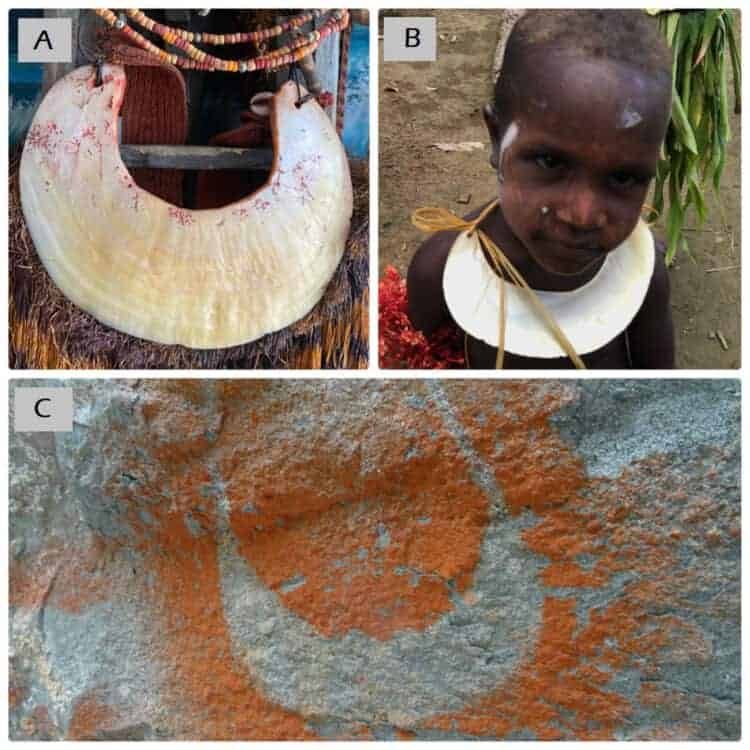
via Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology, 08 December 2020: A new paper by Tsang et al. provides a rare ethnography of rock art sites in Papua New Guinea, revealing the story of shell jewellery and how they were traded over long distances.
Since 1909, patrol officers, anthropologists, archaeologists, and others have identified evidence of a pre-contact trading network linking New Guinea with the Torres Strait. Current research in the Lower Sepik River Basin reported various ethnographic descriptions relating to cultural material objects stenciled on various rock art sites in Auwim, Upper Karawari-Arafundi region, East Sepik, Papua New Guinea (PNG). In addition to the rock art, the broader area has one of the most environmentally intact freshwater basins with lowland rainforests in Melanesia, and is famous for its architectural carvings and spirit houses. This paper reports new research that articulates local ethnographic knowledge about rock art with the art-work itself. The rock art panels contain a wide range of stencils primarily consisting of hands but also, importantly, several objects, one of which is the kina, gold-lip pearl (Pinctada maxima) shell. The kina shell stencils are, among other things, indicative of the remarkable distance over which the shells were traded and traditionally used. The Auwim case study is important because it is one of the relatively few sites across PNG for which we still have ethnography of rock art and therefore provides us with important insight into the past-present rock art practices and, concurrently, notions of cultural continuity.