via Anthropological Science, 07 October 2020: A new paper examines the 2,700-year-old bones of the Escalon Man, named after a cave site near Surigao. Analysis of the bones suggest the Escalon Man was part of the Austronesian migration of agriculturalists from Taiwan.
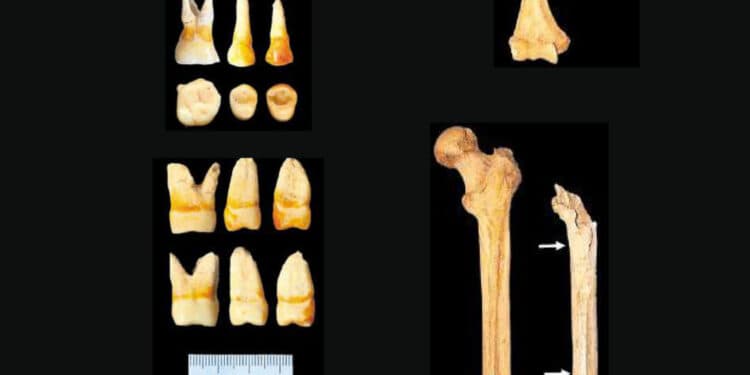
We examined fragmentary human skeletal remains from Escalon Cave near Surigao City, northeastern Mindanao, the Philippines, with respect to the morphology of bones and teeth, radiocarbon dating, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. These remains contained parts of the left temporal bone, the right humerus, the right femur, the upper right first and second premolars, and the first molar. They are presumed to belong to an early-middle adult male, whom we named the Escalon Man. Using the femur sample, we estimated the 14C date of the individual at 2692 ± 39 years BP (uncalibrated). His stature, estimated from the maximum femur length, was about 170 cm—this makes him much taller than the Aeta and the Mamanwa, who are indigenous negrito hunter-gatherers of the Philippines. The femur is sturdy and shows well-developed muscle markings. Numerous narrow grooves on the humerus were found in close proximity to each other, but we could not prove whether these are artificial cut marks made by humans with sharp-edged tools or scratches from some non-human entity. The mesiodistal crown diameters of the molar and premolars are large and resemble those of native Oceanians. Analysis of mtDNA haplogroup was carried out using a DNA sample extracted from a molar. A next-generation sequencer was used to determine the nucleotide sequences of the mtDNA genome. The results indicated that the Escalon Man belongs to the haplogroup E1a1a, which is known to be the marker of Austronesian-speaking agriculturist populations that originated in Taiwan and spread southwards through the Philippines to the Western Pacific, since about 4000 BP. Thus, the Escalon Man was likely a member of the late Neolithic or early Metal Age agriculturist peoples who settled in northeastern Mindanao and who may be the ancestors of the territory’s present-day occupants, such as the Manobo.
See also